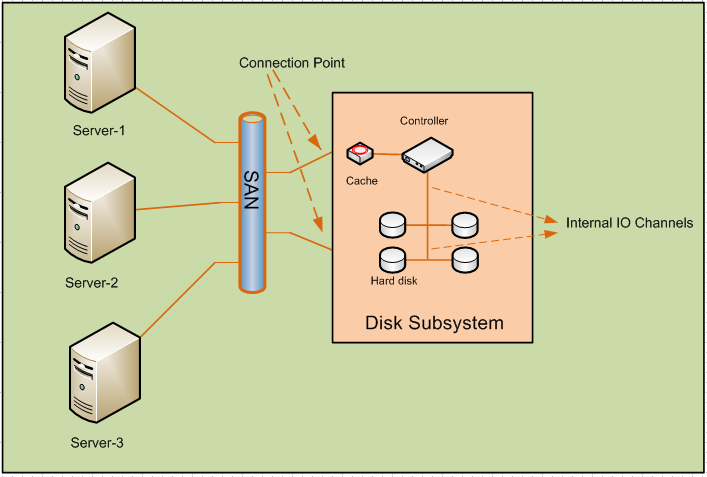
Every intelligent Disk subsystem consists of the below components.
2.Connection Points:- Servers are connected to Disk subsystem via connection points. Each subsystem must be connected more than one connection point to provide redundancy. Small Storages have one or two connection points and 6 to 8 hard disks.
3.Controller:- Disk controller are used to handle write and read operation to/from hard disks. With the help of controller, entire disk array appeared as one virtual hard disk to the servers.
Server sends the blocks of data to the
controller and its controller responsibility to distribute the data to internal
hard disk.
4.Hard
disk:-This is the place where actual data is stored. It is very
critical to choose the size of the Hard disk as it will limit overall maximum
capacity of the storage. More disk in the storage means more read/write heads
which will increase the throughput but then maximum capacity of the system will
reduce. Application with high throughput will require hard disk with smaller
space.
5. Internal IO channels: -
It can use vendor proprietary methods or standard IO method i.e SCSI, FC etc. to connect the controller and internal hard
disks.
There are various design methods of Internal
IO channel in order to provide redundant path between controller and hard
disks.
- Active: - Every hard disk is connected to controller only via single IO channel. If it is broken hard disk will be isolated from Controller.
It is the cheapest and simplest method to provide the connectivity but
not recommended as there is no redundancy.
- Active/Passive: - There are two traces of IO channel but only one path is active at a time. If primary link is down then controller will use backup link to read and write data to the hard disks.
- Active/Active No- Load Balancing :- Both the Channel traces are active but hard disk is only using one trace and keeping the other channel as backup.
As shown below Channel-1 is active only for hard disk 1 -3 whereas it is
used as backup for Hard disk-2 and 4. Similarly Channel-2 is active for Hard
disk 2and 4 and is used as backup for Hard disk1-3.
- Active/Active Load Balancing: - All hard disks are connected to controller via two separate IO channels and both the channel is used to perform read and write operation by the controller.
It is the best method to provide high fault tolerance.
6. Cache:- It is used by the controller to increase the read and write speed. There are two types of cache.
- Cache on the hard disk:- Generally the speed of IO channel are higher than the speed at which controller can write on the hard disk. So the data is being cached by the hard disk to make IO channel free and can be used for the data towards other hard disks.
- Cache on the controller:-Controller has its own cache which caches all the data sent by the servers and allow other servers to send data on the free channel. Controller has its own battery to protect data lose due to power failure.




No comments:
Post a Comment